120V or 240V Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations: What's Single-Pole vs Double-Pole, 2-Wire, 3-Wire or 4-Wire?
When upgrading from a mechanical dial to a smart thermostat on a baseboard heating system, many homeowners quickly realize: the wiring setup is not the same as the 24V HVAC thermostats used in furnaces or heat pumps.
Baseboard heaters in North America typically run on either 120V or 240V line voltage, and the thermostat wiring can be single-pole or double-pole, with 2-wire, 3-wire, or 4-wire connections.
If you’re installing a smart thermostat, understanding these terms isn’t just technical trivia—it’s the difference between a safe, working installation and one that won’t power up at all.
1. Baseboard Heater Voltage: 120V vs. 240V
Before discussing poles and wires, it’s essential to understand voltage differences:
- 120V Baseboard Heaters
- Common in smaller rooms, apartments, or older homes
- Draw higher current for the same wattage compared to 240V
- Often paired with double-pole thermostats to fully cut power (L + Neutral)
- 240V Baseboard Heaters
- Standard in most U.S. and Canadian homes for larger spaces
- More efficient for high-wattage loads since current is lower
- Frequently controlled with single-pole thermostats, cutting only one hot leg
🔎 Pro tip: Check your breaker rating and wiring label before buying a thermostat. A 240V heater on a 120V thermostat will not work—and may be unsafe.
2. Single-Pole vs Double-Pole Thermostats
This is where most confusion begins. In simple terms:
- Single-Pole Thermostat
- Interrupts only one hot leg (L)
- The other leg (L2 or Neutral) remains connected at all times
- Heater is technically always energized, but off when thermostat is open
- for both with 120V & 240V heaters
- Phrase: “single-pole thermostat cuts only one line”
- Double-Pole Thermostat
- Interrupts both legs (Hot + Neutral for 120V, or L1 + L2 for 240V)
- Provides a complete circuit cutoff → safer, often required by electrical code
- Common in 120V heaters, but also used in 240V installations
- Phrase: “double-pole thermostat provides full disconnect”
✅ For smart thermostats:
Most models are single-pole in function—because they require both L and N input for their electronics, but typically only switch one L output to the heater. That means they behave like a single-pole thermostat.
3. Thermostat Wiring Types: 2-Wire, 3-Wire, 4-Wire
Depending on your old thermostat, you may encounter:
- 2-Wire Thermostat
- Simplest form, usually for single-pole
- Just an on/off switch for one leg of the line
- No neutral = ❌ incompatible with most smart thermostats
- 3-Wire Thermostat
- Traditional thermostat, but Smart ones like EcoNet-BH Smart Baseboard Thermostat also supports
- Provides line, load, and pilot/indicator connections
- 4-Wire Thermostat
- Typical for double-pole
- Two wires in (Line L1 + Neutral), two wires out (Load L1 + Neutral to heater)
- Smart Baseboard Thermostat Mainly Supports
- Ensures complete disconnection
4. Why Smart Thermostats Need L + N
Unlike old manual thermostats, smart thermostats require continuous power for their electronics, Wi-Fi/Zigbee chips, and display. This is why Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations are different from low-voltage HVAC thermostats:
- A line-voltage smart thermostat needs:
- L (Line/Hot)
- N (Neutral)
- Traditional 2-wire thermostats simply interrupt power without supplying neutral, which makes them incompatible with most smart models.
👉 This is why you often see the requirement: “Neutral wire required” in smart thermostat manuals.
5. Smart Thermostat = Single-Pole Behavior
In most Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations, the smart thermostat:
- Takes L + N in (to power itself)
- Outputs only switched L to the heater
- Heater’s Neutral goes directly to the heater
This means the smart thermostat only breaks one leg of the circuit—just like a single-pole thermostat.
🔎 While this is common and safe for many 240V systems, electrical codes in some regions still prefer or require double-pole disconnect for safety. Always check your local code.
6. Wiring Diagrams
A) Understanding the 120V Smart Baseboard Thermostat Wiring Schematic
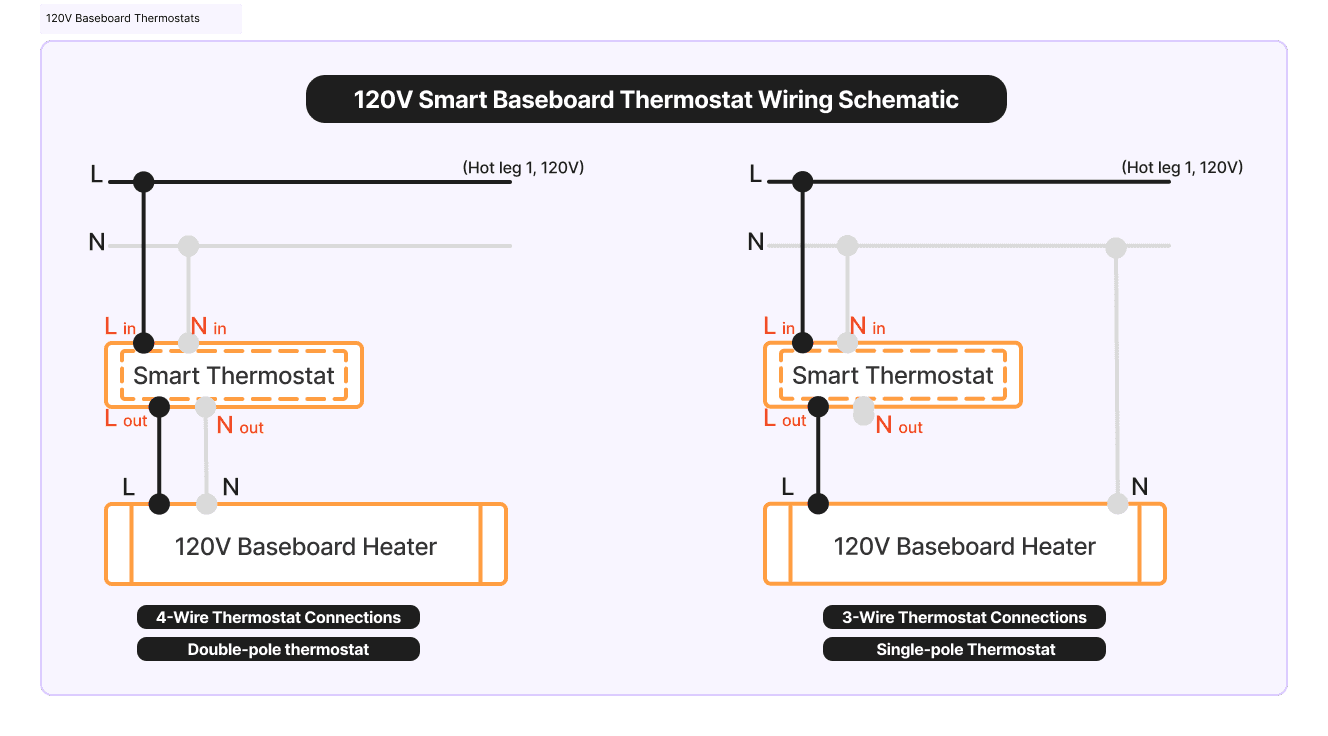
The diagram above shows two common wiring methods used in Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations for 120V systems:
- Left: 4-Wire Double-Pole Thermostat
- The thermostat has Line in / Line out and Neutral in / Neutral out, for a total of 4 wires.
- Both the hot (L) and neutral (N) are switched through the thermostat.
- When turned off, the circuit is fully disconnected, providing maximum safety.
- This is the traditional double-pole thermostat wiring, often required by code.
- Right: 3-Wire Single-Pole Thermostat
- The smart thermostat uses L in and N in to power its electronics.
- Only the hot leg (L) is switched to the heater via L out, while neutral goes directly to the heater.
- This means the thermostat behaves as a single-pole device, interrupting only one leg of the circuit.
- Most modern smart thermostats use this wiring method, since they require a neutral connection for continuous power.
⚡ Key Difference:
- Double-pole (4-wire) = safer, complete circuit cutoff.
- Single-pole (3-wire) = common for smart thermostats, only cuts one hot leg but keeps neutral connected.
**B) Understanding the 240V Smart Baseboard Thermostat Wiring Schematic
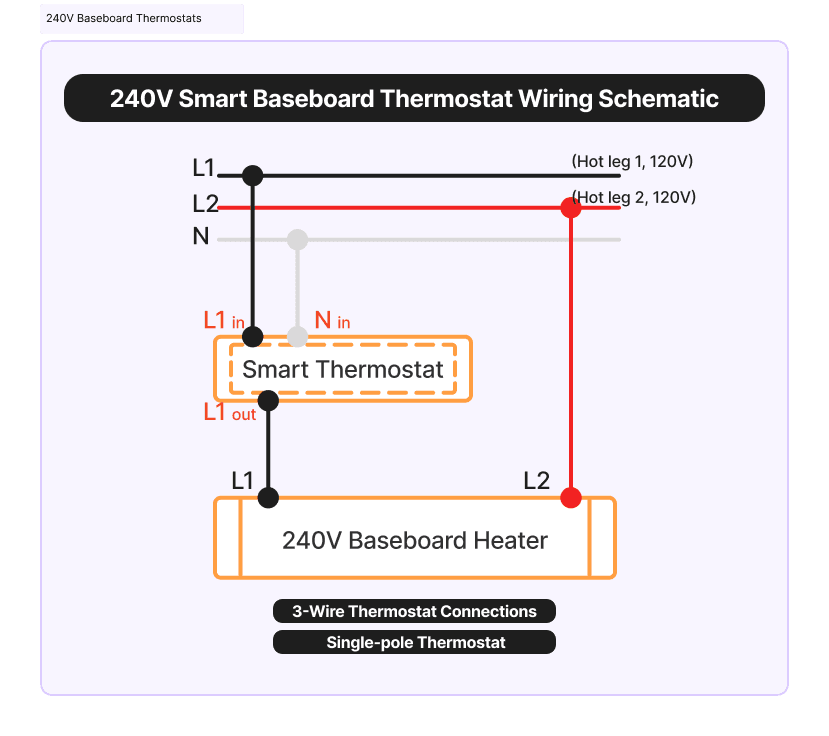
This diagram illustrates how a 240V baseboard heater can be controlled using a smart thermostat in a typical Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installation.
- Power Supply (L1, L2, N)
- 240V heating systems use two hot legs: L1 (Hot leg 1, 120V) and L2 (Hot leg 2, 120V). Together, L1 and L2 provide 240V to the heater.
- Neutral (N) is not required by the heater itself, but the smart thermostat needs a neutral connection to power its internal electronics.
- Smart Thermostat Connections
- L1 in / L1 out: The thermostat switches only one hot leg (L1) to the heater.
- N in: Neutral powers the thermostat’s electronics.
- Output: Heater receives switched L1 and the direct L2, creating a 240V supply.
- Behavior = Single-Pole Thermostat
- The thermostat only interrupts L1.
- L2 remains always connected, so the heater always has one hot leg live.
- This makes the smart thermostat behave as a single-pole thermostat, not a double-pole disconnect.
7. Which Wiring Type Do You Have?
- If your wall thermostat has 2 wires only → It’s a simple single-pole, not usable for most smart thermostats.
- If you see 4 wires → You have a double-pole thermostat, which can usually be adapted to a smart single-pole thermostat installation.
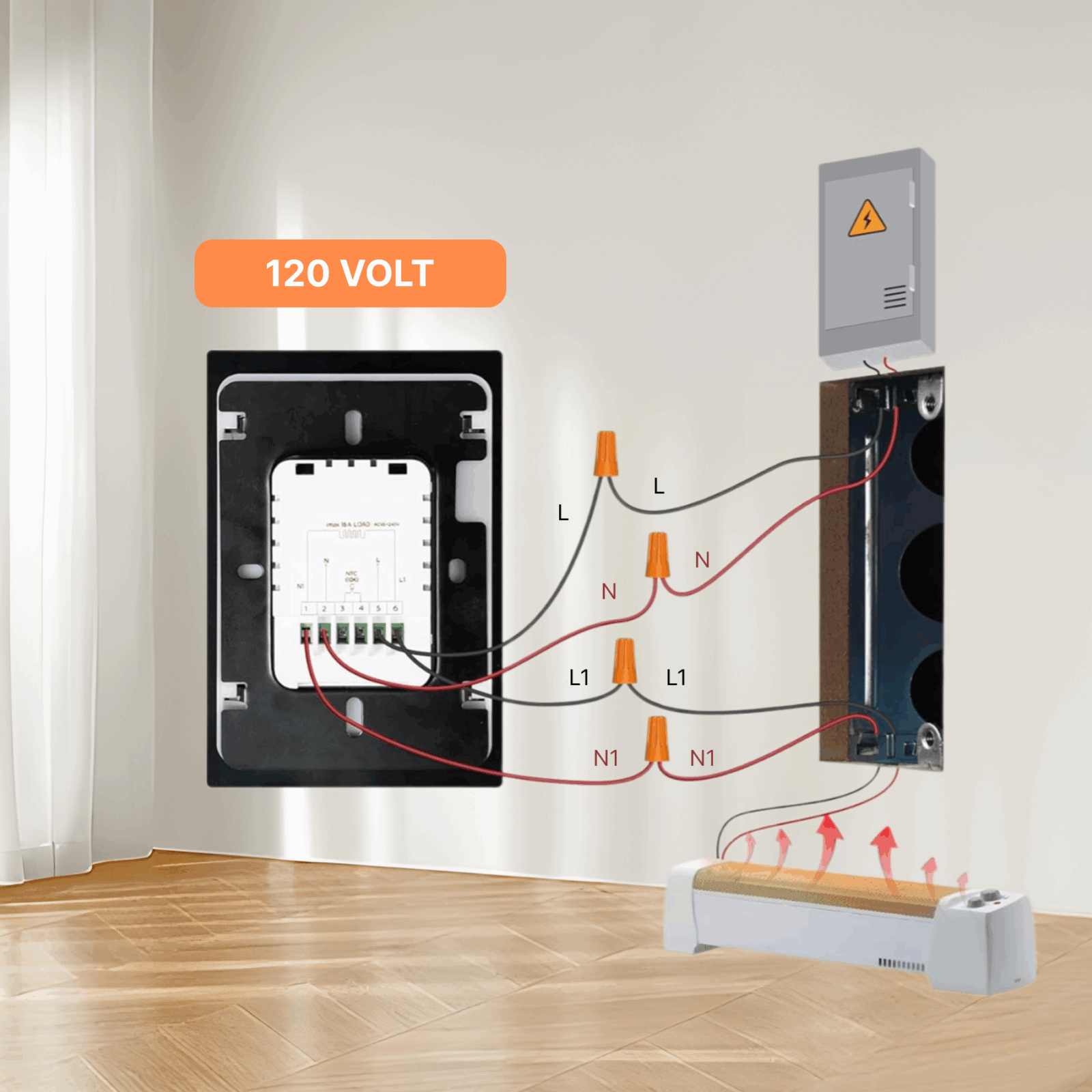

- If you see 3 wires → Likely a pilot light or fan integration; check manufacturer specs.
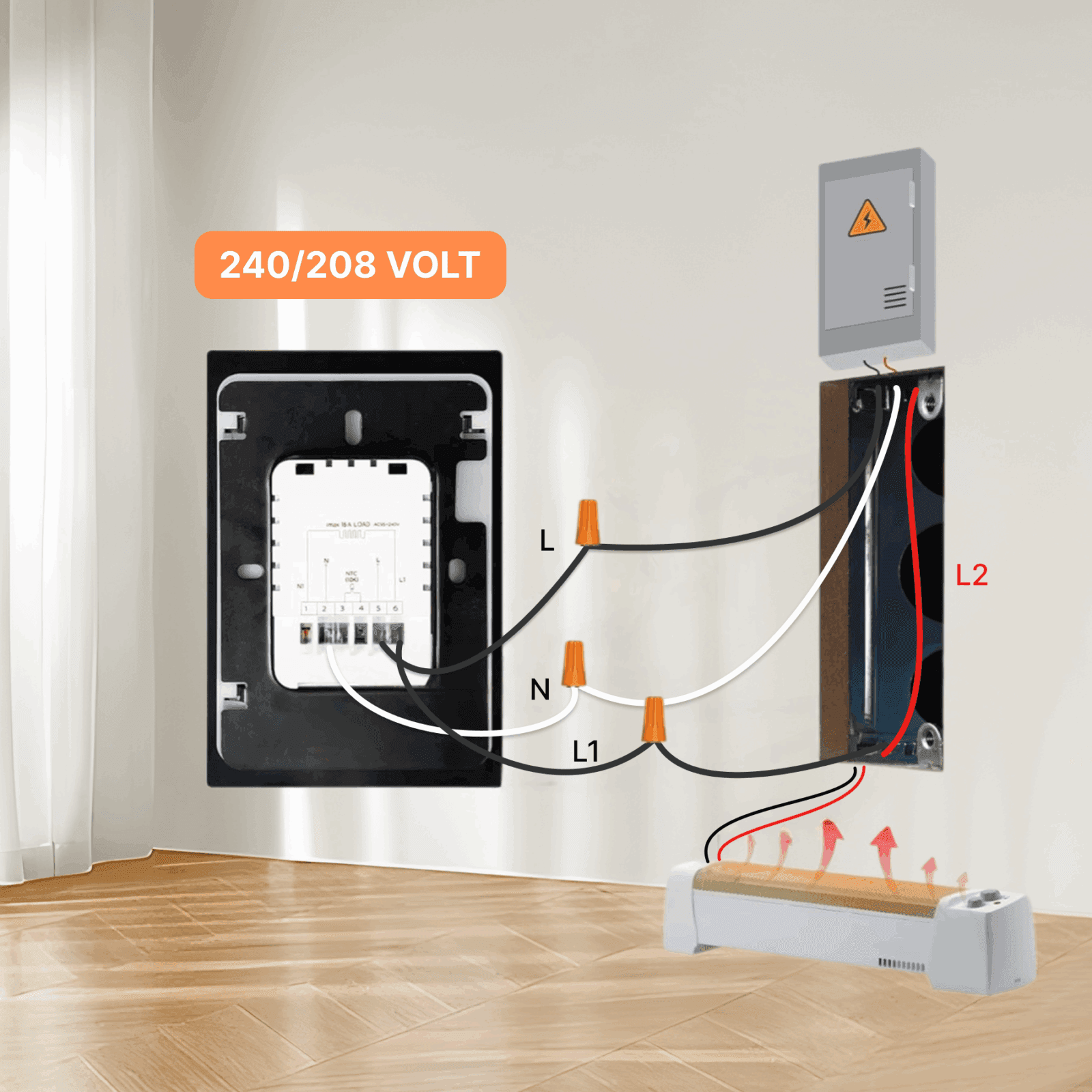
8. Safety and Code Considerations
When dealing with line-voltage wiring (120V / 240V), always remember:
- Double-Pole = Safer Disconnect In many regions, building codes recommend or require double-pole thermostats for complete circuit cutoff, especially on 120V heaters.
- Smart Thermostats = Single-Pole Behavior Most smart thermostats only break one leg (L), leaving the other leg always connected. While this is normal, it’s not a full disconnect.
- Neutral Required If your installation has only two hot wires and no neutral, you may need to run a new cable or choose a thermostat specifically designed for 2-wire operation (rare in the smart market).
⚡ Pro Tip: Always verify wiring with a multimeter and check your local electrical code. If in doubt, hire a licensed electrician.
9. Compatibility by Wiring Type
Here’s a simple compatibility table for Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations:
| Wiring Type | Pole Type | Typical Use Case | Smart Thermostat Compatible? | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Wire | Single-Pole | Old dial thermostats | ❌ Not compatible | No neutral → smart thermostat won’t power |
| 3-Wire | Single-Pole | Traditional baseboard systems | ✅ Yes (As Double-Pole) | Neutral required for smart thermostat |
| 4-Wire | Double-Pole | Modern baseboard systems | ✅ Yes (as single-pole) | Neutral required for smart thermostat |
10. Choosing Between Single-Pole and Double-Pole for Smart
- If you want safety & full disconnection → Stick to double-pole mechanical thermostats.
- If you want smart features (Wi-Fi, Zigbee, automation) → Expect single-pole operation, since most smart thermostats only switch one leg while using neutral for power.
👉 The best path is to upgrade to a smart thermostat that matches your voltage (120V or 240V) and wiring configuration, then supplement safety with a breaker or dedicated disconnect switch.
11. Why Upgrade Now?
- Save 10–20% on heating costs each winter (DOE data)
- Remote control & automation = comfort without waste
- Integration with smart homes (Home Assistant, Zigbee2MQTT, Alexa, Google)
- Future-ready utility upgrade as more households adopt smart energy management
🔚 Conclusion
Whether you’re running a 120V baseboard heater in a small apartment or a 240V system across a large home, understanding the difference between single-pole vs double-pole and 2-wire, 3-wire, or 4-wire setups is essential before installing a smart thermostat.
Baseboard Heater Smart Thermostats Installations aren’t difficult—once you know your wiring type and match it with the right thermostat.
📢 Upgrade with Grus.io
Ready to modernize your baseboard heating?
Check out the EcoNet-BH Smart Baseboard Thermostat:
- ✅ Designed for Both 120V and 240V baseboard heaters
- ✅ Open Smart Home Systems
- ✅ Smart scheduling and remote control
- ✅ Easy 4-wire install, no C-wire required
👉 Upgrade today, and enjoy smarter, safer heating this winter.
Comments
Post a Comment